Potassium Citrate
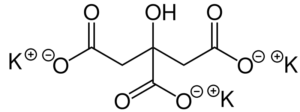
Origin
Potassium citrate is synthesized through a chemical reaction where potassium bicarbonate or potassium carbonate is introduced to a citric acid solution. This process continues until there is no more effervescence, followed by filtering and evaporating the solution to form granules.
Also Known As
Potassium citrate is recognized by its chemical name but is also referred to by several other names:
- Tripotassium citrate
Usages
This compound is primarily utilized in the medical field to prevent kidney stones that develop from excessive amounts of uric acid or cystine. Additionally, it serves as a food additive, playing a crucial role in regulating acidity levels in various food products.
Overview
Potassium citrate is characterized by its white color, lack of odor, and crystalline form. It has significant applications both in healthcare and the food industry due to its property of controlling acidity levels. Its key features include:
- Odorless and white crystalline appearance
- Preventative treatment for certain types of kidney stones
- Regulatory use as a food additive to manage acidity
Common Dosage
The typical dosage of potassium citrate for the treatment of hypocitraturia is 150 mg per day. This dosage is designed to effectively manage the condition while ensuring safety and minimizing potential side effects.
Summary
Potassium citrate is an invaluable chemical compound with wide-ranging applications, from medical treatments to food production. It is synthesized through a chemical process involving potassium bicarbonate or carbonate and citric acid. Key takeaways include:
- Effective in preventing kidney stones related to uric acid or cystine
- Used as a food additive to control acidity
- Typical dosage for hypocitraturia is 150 mg per day
For more information call Nutrasky today.







